Financial Planning & Analysis
Use numbers to make the most advantageous choices and steer the company toward its goals.
Fill out the form to request information

Change is less daunting when you have everything under control
The Management Control area in Fluentis ERP represents a strategic, high-value tool that enables highly integrated and results-oriented companies to monitor the achievement of their objectives through cost and variance analysis.
Modules and Features
All the tools for:
Defining a multidimensional structure of business units to support multiple simultaneous analyses for maximum flexibility.
Establishing business strategy and planning through a budgeting system to compare with the actual reporting system.
Automatically allocating common costs among various cost centers through the cost driver system.
Integrating accounting data with management-type records, valued, for example, in work hours or number of units, which are captured by production, logistics, assets, or active/passive document cycle modules. The integrated pricing system in the module automatically values these quantities in economic terms based on the calculations that occur within the system to assess the cost of individual units or entire cost centers.
Compiling a comprehensive budget that integrates accounting data through a system of freely aggregatable semi-annual balances through reclassifications, cost center movements, allocations, and apportionments, various indices, and rates for physical quantities.

The strategic role of Management Control in managing change in an era of uncertainty
High Automation
High automation in the allocation of common costs and transfers between business units is achieved through a highly powerful cost driver system. Numerous logics are available, and it is possible to define processing priorities, for example, first processing the allocation of common costs not assigned by general accounting, and subsequently, after the initial allocation, transferring auxiliary centers to production centers, thus valuing sales orders.
Ease of Use
The Controlling module also allows for simplified use to support purely accounting analysis and processing. Valuable information can be obtained through semi-annual accounting closures with related adjustments and corrections, balance reclassifications according to models freely defined by the user, and comparisons between reclassifications with the analysis of variations.
Perfectly Integrated
Integration occurs not only with the General Accounting and Analytical Accounting modules, but also with Production and Logistics for the integration of physical movements, such as labor hours and quantities of raw materials used in production.
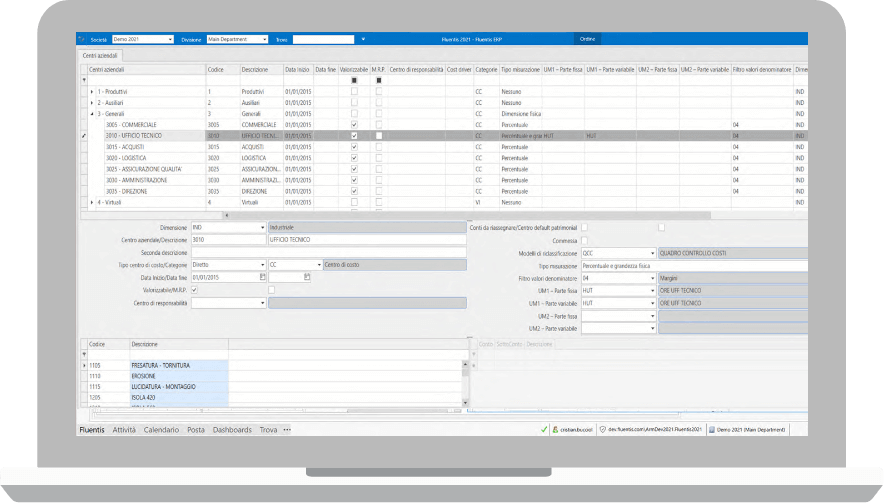
Maximum flexibility in defining business units
(A modern evolution of cost and profit centers, capable of accommodating both types of transactions).
The multidimensional logic allows for conducting multiple analyses in parallel, such as a full-costing analysis and a specific analysis related to a strategic investment, where accounting transactions are simultaneously assigned to centers referring to different aggregates.
Configurable structure and groupings.
Specific logics for general costs not initially assigned by general accounting and for managing asset accounts within business units.
The units can accommodate physical quantities such as labor hours and provide data for the calculation of rates (Euro/hour) for the valuation of quantities by interfacing with accounting data reclassification models.
Dimension logic that allows for multiple concurrent analyses, starting from the same accounting transactions automatically assigned to different dimensions.
Identify product and project margins

Definition of business units and Accounting Relationships
The definition of the business unit plan and its relationships with the accounting chart of accounts are crucial in the field of Controlling. The primary objective is to identify the margins of products or projects.
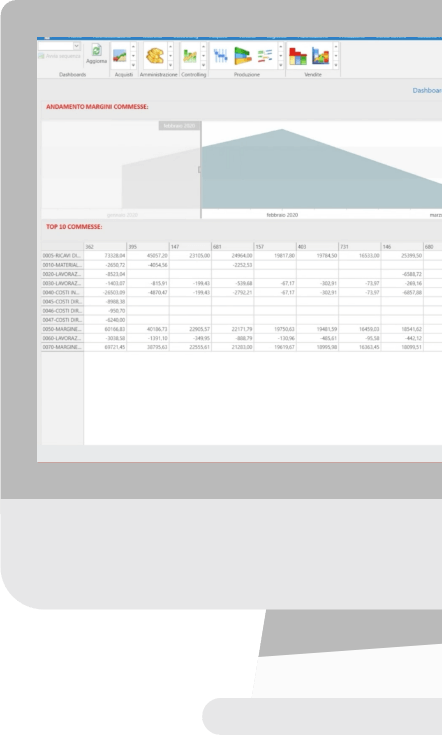
Tools for analysis in Business Controlling
Various tools are used to analyze data in Business Controlling. These include reports, data cubes, and dashboards, which allow you to view the results of corporate economic reporting models. Center Economic Reports analyze the cost components of parametric rate structures.
The importance of data analysis
Data analysis is essential in Business Controlling.
This analysis provides an overview of economic performance and production costs, facilitating the decision-making process.

What our customers say about Fluentis

Fluentis ERP actively contributes to our company like that invisible thread that keeps us all united, efficient, and focused on our corporate mission.
- Monica Maretti, CFO
Mareco Luce Srl
The Application Modules
Intra-Year Closings
This module allows you to process data from the general ledger without interfering with it. It enables unlimited analyses that can support both the subsequent processing of periods under analysis by integrating production data (physical measurements) and other management-related entries, and simple accounting analyses of period balances or reclassifications.
Closings allow for the processing of specific adjusting and settling entries (non-accounting) related to the specific time period. These entries include accruals, deferrals, depreciation, outstanding invoices, inventory balances, and other freely definable entries (for provisions such as bad debt or risk funds).
Intra-Year Closing Processing
- Ability to process by distinguishing between business divisions and analysis areas (Budget, actuals, etc.) to support different analysis scenarios.
- Independent recovery of economic and patrimonial movements.
- Option for simultaneous processing of adjustment and integration entries.
Consolidation
A useful procedure for processing the closings of different companies in the database to neutralize intra-group economic (costs – revenues) and patrimonial (credits – debts) components by consolidating overall costs and revenues. It allows for obtaining a group balance sheet.
Inventory Accounting
The procedure retrieves data from the warehouse and allows for inventory valuation using different criteria, including the related non-accounting entry within the selected closing.
Resumption of Asset Depreciation
The procedure reads the fixed asset cards and calculates depreciation similar to that in the administrative module. However, it performs a non-accounting entry linked to the selected closing and considers the period under closing in the calculation.
Adjustment/Integration Entries
- Allows for the separate execution of adjustment and integration entries (accruals and deferrals) at a later time after creating the closing.
- The calculation and entries are non-accounting to avoid influencing the general ledger.
- The logic takes into account the period under closing, comparing it with the range of dates of economic relevance for the cost or revenue set within each accounting entry.
Entries for Cost Drivers
Allows you to use the logic defined in cost drivers for creating transfer entries in analytical accounting related to the selected closing.
Purchase and Sales Valuation
In the reference period under closing, it searches for delivery notes (BOLs) and invoices not yet entered in the general ledger and reconstructs their values for the closing. This is a kind of non-accounting outstanding invoices.
Intra-Year Balance Sheet Printing
A practical and quick direct printout of the closing to obtain the balance sheet for the period under closing without further reclassifications.
Balance Sheet Reclassifications
The functionalities of this module allow you to process intra-year closings by reclassifying accounting balances or the movements of business centers through reclassification models freely definable by the user. However, some predefined models are also available for immediate use. The reclassification model allows for any representation without limitations on the number of levels and sublevels, and it manages summations and other mathematical operations to calculate ratios and other useful indices. You can also compare different reclassifications, highlighting percentage variances.
Reclassification Models
You can create a completely customized model or modify one of the predefined models. In the model, everything is editable and customizable, from the representation of the reclassification that can take place on an unlimited number of sub-levels to the formulas for calculating sums or ratios, to the mapping of the general ledger’s chart of accounts. This last connection, in particular, allows you to relocate every general ledger account and business center within the scheme, regardless of the original chart of accounts structure, whether keeping the debit/credit sections combined or separating them to position them separately in different parts of the scheme.
Reclassification Processing
Once you have defined your reclassification model, the processing will be very fast with just a few simple steps: you indicate to the software which closing to process, according to which reclassification model, and you’re done!
Reclassification Comparison
You can compare an unlimited number of reclassifications, highlighting percentage variances for each item in the model, both relative to different elaborations and as a percentage of the total items for each elaboration.
Reclassification Printing
Useful for obtaining hard copy prints of the elaborations.
Budgeting
This module in the Control Management Area allows you to create an accounting budget that can be compared with the actual analyses derived from intra-year closings and other analytical accounting processing, such as cost drivers, leading to the analysis of variances between budget and actuals.
Non-Accounting Budget Entries
The available commands allow you to freely add accounting entries to the budget linked to general ledger accounts, business centers, and projects.
Product Cost
This is a fundamental tool in Management Control for monitoring a company’s margins. It allows you to value the cost based on various versions of the Bill of Materials (BOM), valuing them at the last/average/standard cost or by management areas. The data is stored at the processing date to enable the analysis of a historical series of cost trends. The module also allows you to update the last cost, standard cost, or next year’s standard in the item master data.
Cost Calculation
This process calculates the simulated product cost for selected items.
Cost Recalculation
This process updates the last and average costs of selected items.
Assembly Valuation
This report displays the detailed cost breakdown of assemblies by exploding the BOM of the item into its individual components.
Sales Forecast
This is one of the fundamental tools for planning and controlling a company’s sales activity. It helps determine what the company will sell in a given period. Both value and volume forecasts are managed, for individual items or product families. Various simulation forecasts can be analyzed through versions. Their consolidation provides input for the generation of Orders.
Sales Data Retrieval
This process generates automatic Sales Forecasts and Seasonal Patterns based on historical data from sales area documents: Customer Orders, Delivery Notes, and Sales Invoices.
Product Families
You can define forecasts for groups of homogeneous products. Forecasts for each individual product, a component of a specific family, will be determined based on the importance percentage assigned to the component itself.
Consolidation
This activity is necessary to consider forecasts as input for the generation of procurement orders.
Management Accounting
The module is the heart of the Control Management area and contains analytical period processing features that can automatically calculate all the necessary cost allocations, business center allocations (e.g., auxiliary to productive, etc.), and project costing. It also captures physical movements from production or inventory (e.g., labor hours, quantities of raw materials used, etc.) and determines the valuation rates for physical quantities based on predefined parameters and settings.
Management Accounting Entries
- Extra-accounting entries allow the manual entry of movements.
- Entries for physical movements allow manual entry of measurable movements, such as labor hours or raw material quantities.
- Standard rates for business centers allow direct intervention in the valuation rates of physical quantities (e.g., Euro/hour or Euro/piece).
Period Processing
This represents one of the fundamental features and triggers automation for managing physical movements (e.g., labor hours or raw material pieces used) through the calculation of valuation rates, the calculation of specific depreciation for controlling (reflecting specific logic not influenced by tax regulations, such as perpetual or actual percentage calculations), the calculation of cost driver attributions and allocations, and the processing of project cost reports.
Data Capture from Production
This allows the interception of movements entered in the production area to declare labor hours, machine times (per actual or standard cycle or phase), costs of internal/external operations (at average, last, or standard cost), and include them in management accounting processing and project cost reports.
Data Capture from Sales Invoices
This allows processing commission agents and applied discounts from the sales cycle.
Business Center Rate Update
Utility for recalculating the rates (e.g., Euro/hour or Euro/piece) used for valuing physical quantities (e.g., labor hours or raw material pieces).
Master Consolidation
A very interesting utility for generating a consolidated report for control data within a master company (parent company) present in the database, retrieving data from secondary companies within the same database.
Management Accounting Reports
- Management Accounting Statement: Concerning movements of management accounting.
- Depreciation Control: Relating to specific depreciation calculations in the control module (not influenced by tax regulations).
- Project Consolidated Report: Results of orders/projects.
View and Archive
- Archiving (History):
- Flows of physical movements from production.
- Specific depreciation for Control.
- Entries in the management accounting journal.
- Indices for rate determination.
- Visualization:
- Accounts not used in control: Serves to reconcile the general ledger and control; for example, accounting depreciation is bypassed and replaced by the specific logic of the control module, but it is always possible to verify reconciliation.
- Control Values: Reconciliation panel for values from the general ledger, the allocations made by the cost drivers, and the adjustments needed to reconcile values subject to different logics.
- Project History:
- Archive form for reading and storing data related to orders/projects and related to physical movements, management accounting entries, and consolidated progress reports.
Discover how Fluentis ERP
can transform your business
15-day free trial | No automatic renewal | Instant access
Contact us for more information
Get in touch with us if you:
- Are a SMB in Manufacturing, Distribution, or Services
- Need to streamline and digitalize your business processes
- Want to take advantage of the benefits of a native cloud solution
- Want to replace your non-integrated softwares with a unified ERP platform
+1 281 404 1726
Chat with us